木
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual[edit]
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Alternative forms[edit]
- In Hong Kong and Taiwan, when 木 is at the bottom of a character, it is written as 朩 without a hook instead of 木 itself.
Han character[edit]
木 (Kangxi radical 75, 木+0, 4 strokes, cangjie input 木 (D), four-corner 40900, composition ⿻十𠆢)
- Kangxi radical #75, ⽊.
Derived characters[edit]
- Appendix:Chinese radical/木
- 休, 㕲, 𡉿, 𡯐, 𫹎, 𪫟, 𢪮, 沐, 狇, 𫐠, 炑, 牀, 𭷉, 𤘬, 𬍓, 𦙣, 𠣛, 𬎳, 𤱃, 𤴷, 𪽻, 𥄢, 𪿈, 𥝰, 𠚐, 䊾, 𦐔, 蚞, 𮗼, 䝗, 𮠛, 鈢, 𩵦(𫠏)
- 禾, 米, 𠫡, 呆, 㚓, 宋, 𡭢, 𡵬, 床, 㦿, 𬇏, 𠕖, 采, 𦊋, 罙, 䂞, 穼, 䍒, 𬺜, 𦊧, 臬, 𠡷, 㕖, 集, 雬, 𡩎, 渠, 琹, 喿, 㮡, 髤, 䲷, 䴢, 燊, 築, 蘃, 蘖, 雧, 䯂
- 䢶, 相, 𡉣, 𪥄, 𢌶, 𢗦, 𤆰, 𤯃, 𦕂, 𧉓, 𧴿, 螙, 凩, 閑(闲), 困, 耒, 來, 𣸑, 𠎀, 𠍇, 𤨪, 𤚦, 鬱
Descendants[edit]
- Japanese: 𛀧 (Hentaigana)
References[edit]
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 509, character 1
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 14415
- Dae Jaweon: page 888, character 13
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 2, page 1149, character 6
- Unihan data for U+6728
Chinese[edit]
| simp. and trad. |
木 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin[edit]
| Historical forms of the character 木 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
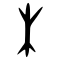
|

|

|

|

|
Pictogram (象形) – a tree: branches on top, roots on the bottom (more visible in earlier forms).
Etymology[edit]
No known cognate exists. It can perhaps be compared with Proto-Karen *məŋᴮ (“trunk (of a tree); firewood”) (Starostin) or Proto-Lolo-Burmese *ʔmuk (“stump (of a tree)”) (Schuessler, 2007).
The common Sino-Tibetan root for “tree; wood” is *siŋ ~ sik, represented by 薪 (OC *siŋ, “firewood”).
Pronunciation[edit]
Definitions[edit]
木
- tree; woody plant
- wood; timber (Classifier: 條/条 c; 塊/块 c; 嚿 c; 轆/辘 c)
- wooden
- (literary or in compounds) coffin
- 就木 ― jiùmù ― to die (literally, “to enter one's coffin”)
- 原壤登木曰:「久矣予之不托於音也。」 [Classical Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Book of Rites, c. 4th – 2nd century BCE, translated based on James Legge's version
- Yuán Rǎng dēng mù yuē: “Jiǔ yǐ yǔ zhī bù tuō yú yīn yě.” [Pinyin]
- Yuan Rang got up on the coffin [of his mother] and said, "It is long since I sang to anything."
原壤登木曰:「久矣予之不托于音也。」 [Classical Chinese, simp.]
- simple; plain; slow; emotionless; wooden
- numb
- a surname
- (Mandarin, neologism, slang) Eye dialect spelling of 沒/没.
- 有木有 ― yǒumùyǒu ― innit, damn right
Synonyms[edit]
- (tree):
- (wood):
| Variety | Location | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 木頭 | |
| Mandarin | Beijing | 木頭 |
| Taiwan | 木頭 | |
| Jinan | 木頭 | |
| Xi'an | 木頭 | |
| Wuhan | 木頭 | |
| Chengdu | 木頭 | |
| Guilin | 木頭 | |
| Yangzhou | 木頭 | |
| Hefei | 木頭 | |
| Singapore | 木頭 | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | 木 |
| Hong Kong | 木 | |
| Yangjiang | 木頭 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 木頭 |
| Hakka | Meixian | 樹料, 木頭 |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 木頭 |
| Northern Min | Jian'ou | 柴 |
| Eastern Min | Fuzhou | 柴 |
| Southern Min | Xiamen | 柴 |
| Taipei (Wanhua) | 柴 | |
| Kaohsiung | 柴 | |
| Yilan | 柴 | |
| Changhua (Lukang) | 柴 | |
| Taichung | 柴 | |
| Taichung (Wuqi) | 柴 | |
| Tainan | 柴 | |
| Taitung | 柴 | |
| Hsinchu | 柴 | |
| Penghu (Magong) | 柴 | |
| Manila (Hokkien) | 柴 | |
| Chaozhou | 柴 | |
| Wu | Suzhou | 木頭 |
| Wenzhou | 木頭, 樹 log | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 木頭 |
| Shuangfeng | 樹 | |
- (coffin):
Compounds[edit]
- 一元木公
- 一木之枝
- 一木難扶/一木难扶
- 一木難支/一木难支 (yīmùnánzhī)
- 一草一木
- 三尺之木
- 三木 (sānmù)
- 三木樓訾/三木楼訾
- 上木驢/上木驴
- 不沉木
- 不灰木
- 不燼木/不烬木
- 不盡木/不尽木
- 不藉木/不借木
- 丘木
- 丫木
- 中間砧木/中间砧木
- 丹木
- 乘木
- 五木
- 五木香
- 亞喬木/亚乔木
- 亡猿災木/亡猿灾木
- 亡猿禍木/亡猿祸木
- 亢木
- 交讓木/交让木
- 人木
- 人非木石
- 人非草木
- 仁壽木/仁寿木
- 仙木
- 任木
- 伐木 (fámù)
- 佳木 (Jiāmù)
- 佳木斯市
- 依艸附木
- 依草附木
- 依麻木 (Yīmámù)
- 倚草附木
- 偉木/伟木
- 做木頭/做木头
- 傑木/杰木
- 僵木
- 入木
- 入木三分 (rùmùsānfēn)
- 兵木
- 冢木已拱
- 凡木
- 凡木蔓
- 刊木
- 划木
- 刳木
- 刻木
- 刻木為吏/刻木为吏
- 刻木為鵠/刻木为鹄
- 刻木爲吏/刻木为吏
- 削木為吏/削木为吏
- 剛木/刚木
- 剛毅木訥/刚毅木讷
- 千頭木奴/千头木奴
- 卉木
- 半灌木
- 原木 (yuánmù)
- 叢木/丛木
- 古木蔽天
- 名木
- 吐木秀克 (Tǔmùxiùkè)
- 呆似木雞/呆似木鸡
- 吾塔木 (Wútǎmù)
- 呆如木雞/呆如木鸡
- 呆木
- 呆木大
- 呆木頭/呆木头
- 呆若木雞/呆若木鸡 (dāiruòmùjī)
- 呆頭木腦/呆头木脑
- 和木
- 哈尼喀塔木 (Hāníkātǎmù)
- 啄木 (zhuómù)
- 啄木鳥/啄木鸟 (zhuómùniǎo)
- 喬木/乔木 (qiáomù)
- 嘉木 (jiāmù)
- 四味木
- 四方木——踢一踢,喐一喐
- 圍木/围木
- 圓木/圆木 (yuánmù)
- 圓木警枕/圆木警枕
- 圖木舒克/图木舒克 (Túmùshūkè)
- 土木 (tǔmù)
- 土木之禍/土木之祸
- 土木之變/土木之变
- 土木之難/土木之难
- 土木偶人
- 土木八
- 土木堡
- 土木工程 (tǔmù gōngchéng)
- 土木形骸
- 土木監/土木监
- 土木身
- 土牛木馬/土牛木马
- 土青木香
- 坑木 (kēngmù)
- 塋木/茔木
- 塚木已拱/冢木已拱
- 塔里木 (Tǎlǐmù)
- 塔里木河 (Tǎlǐmù Hé)
- 墓木
- 墓木已拱 (mùmùyǐgǒng)
- 壞木/坏木
- 壽木/寿木 (shòumù)
- 大木廠/大木厂 (Dàmùchǎng)
- 大興土木/大兴土木 (dàxīngtǔmù)
- 奈何木
- 孤木
- 孤立木
- 宰木
- 寓木
- 寒木
- 寒木春華/寒木春华
- 寸木岑樓/寸木岑楼
- 尋木/寻木
- 小木
- 尖頂木驢/尖顶木驴
- 尖頭木驢/尖头木驴
- 就木 (jiùmù)
- 尺木
- 山啄木
- 山木
- 山精木客
- 山頹木壞/山颓木坏
- 岐木
- 巢木居野
- 布袋木偶
- 帖木兒/帖木儿
- 常春木
- 平地木
- 平衡木 (pínghéngmù)
- 度木
- 庫拉木勒克/库拉木勒克 (Kùlāmùlèkè)
- 庫木巴希/库木巴希 (Kùmùbāxī)
- 建木
- 弦木
- 影木 (yǐngmù)
- 徙木
- 徙木之信
- 徙木立信
- 心如木石
- 心如槁木
- 惡木/恶木
- 惟那木
- 房木
- 托木吾斯塘 (Tuōmù Wúsītáng)
- 抗木
- 扶木 (fúmù)
- 投木報瓊/投木报琼
- 抱木
- 拘木
- 拙木
- 招木
- 拔木
- 拍木勝/拍木胜
- 拗木枕
- 拒門木/拒门木
- 拱木
- 授木
- 接木 (jiēmù)
- 採木/采木
- 掮木梢
- 提線木偶/提线木偶 (tíxiàn mù'ǒu)
- 搆木為巢/构木为巢
- 撞木
- 撞木鐘/撞木钟
- 擋木/挡木
- 擇木/择木 (zémù)
- 擂木
- 擇木而處/择木而处
- 攀蘿附木/攀萝附木
- 攔道木/拦道木
- 攢木/攒木
- 改木
- 故家喬木/故家乔木
- 教猱升木
- 散木
- 文木
- 斧木
- 斫木
- 斬木揭竿/斩木揭竿
- 斬木為兵/斩木为兵
- 斬竿揭木/斩竿揭木
- 斲木
- 斷木/断木
- 斷木掘地/断木掘地
- 旌木
- 旋木雀
- 曲木几
- 木下三郎
- 木三對/木三对
- 木上座
- 木丸
- 木丹
- 木主 (mùzhǔ)
- 木乃伊
- 木乳餅/木乳饼
- 木乾鳥栖/木干鸟栖
- 木事
- 木人
- 木人石心
- 木介
- 木伐
- 木佛
- 木作 (mùzuò)
- 木位
- 木伴哥
- 木佬佬
- 木侯
- 木俑
- 木偶 (mù'ǒu)
- 木假亭
- 木偶人
- 木假山
- 木偶影片
- 木偶戲/木偶戏 (mù'ǒuxì)
- 木偶片
- 木偶衣冠
- 木偶馬/木偶马
- 木像
- 木僕/木仆
- 木僵
- 木僵僵
- 木兔
- 木公
- 木公金母
- 木冊/木册
- 木冰
- 木函
- 木刀
- 木券
- 木刻 (mùkè)
- 木刻水印
- 木刻畫/木刻画
- 木刻符契
- 木劍/木剑
- 木功
- 木化
- 木化九隆
- 木化石
- 木匠 (mùjiàng)
- 木匠帶枷/木匠带枷
- 木匠戴枷
- 木匣
- 木印
- 木印記/木印记
- 木厥
- 木口雕刻
- 木吉 (Mùjí)
- 木吏
- 木呆
- 木吾
- 木呆呆
- 木商
- 木嗩吶/木唢呐
- 木器 (mùqì)
- 木嚼
- 木囚
- 木圖/木图
- 木坡
- 木城
- 木堇
- 木堤
- 木場/木场
- 木塞
- 木壞山頹/木坏山颓
- 木大 (mùdà)
- 木天
- 木夫
- 木天署
- 木夯
- 木夾/木夹
- 木契
- 木奎拉 (Mùkuílā)
- 木奴
- 木妖
- 木威 (Mùwēi)
- 木威喜芝
- 木婚
- 木媚
- 木子
- 木子店
- 木字旁 (mùzìpáng)
- 木孫/木孙
- 木官
- 木客
- 木室
- 木客大冢
- 木客詩/木客诗
- 木客鬼
- 木客鳥/木客鸟
- 木寓
- 木寓馬/木寓马
- 木寓龍/木寓龙
- 木實/木实
- 木射
- 木尺
- 木局
- 木居士
- 木居海處/木居海处
- 木屋 (mùwū)
- 木屐 (mùjī)
- 木屑 (mùxiè)
- 木屧
- 木履
- 木岸
- 木工 (mùgōng)
- 木已成舟 (mùyǐchéngzhōu)
- 木帝
- 木幔
- 木床
- 木店
- 木廂/木厢
- 木廠/木厂
- 木弓
- 木弩
- 木強/木强
- 木強則折/木强则折
- 木彊/木强
- 木形灰心
- 木征
- 木德
- 木心板
- 木心石腹
- 木怪
- 木性
- 木愣愣
- 木戇/木戆
- 木戾
- 木扇
- 木手
- 木拉 (Mùlā)
- 木披
- 木拐梯子
- 木挑
- 木拱
- 木掀
- 木排 (mùpái)
- 木撥/木拨
- 木撲頭/木扑头
- 木數/木数
- 木料 (mùliào)
- 木斛
- 木斤
- 木斧
- 木斫
- 木易
- 木星 (Mùxīng)
- 木曜 (mùyào)
- 木曜日 (mùyàorì)
- 木木
- 木木樗樗
- 木木然
- 木本 (mùběn)
- 木札
- 木末
- 木本之誼/木本之谊
- 木本植物
- 木本水源
- 木朽不雕
- 木材 (mùcái)
- 木杠
- 木杆
- 木杖
- 木杙
- 木李
- 木材工業/木材工业
- 木杵
- 木杷
- 木枕
- 木枋
- 木板 (mùbǎn)
- 木杻
- 木杪
- 木板大鼓
- 木板書/木板书
- 木板畫/木板画
- 木板鞋
- 木柺
- 木柴 (mùchái)
- 木架
- 木柶
- 木柵/木栅 (mùzhà)
- 木柈
- 木柑
- 木柙
- 木柈子
- 木柵門/木栅门
- 木桂
- 木桁
- 木桃 (mùtáo)
- 木格
- 木根
- 木栓 (mùshuān)
- 木栰
- 木梓 (Mùzǐ)
- 木梃
- 木條/木条
- 木梆
- 木械
- 木梗
- 木梢
- 木桿/木杆
- 木梗之患
- 木梗人
- 木棉 (mùmián)
- 木棍 (mùgùn)
- 木棒 (mùbàng)
- 木棲/木栖
- 木植
- 木椎
- 木棧/木栈
- 木棦
- 木椌
- 木棉花
- 木楗
- 木楂
- 木椹
- 木楊城/木杨城
- 木榻
- 木榜
- 木構/木构
- 木槍/木枪
- 木榻穿
- 木樨 (mùxī)
- 木樁/木桩 (mùzhuāng)
- 木槿 (mùjǐn)
- 木模
- 木標/木标
- 木樓/木楼
- 木槽
- 木槨墓/木椁墓
- 木樨花
- 木槽馬/木槽马
- 木橛
- 木樵 (mùqiáo)
- 木樸/木朴
- 木檄
- 木櫝/木椟
- 木櫬/木榇
- 木欒/木栾
- 木正
- 木母
- 木毬使者/木球使者
- 木氣/木气
- 木汁
- 木沉產子/木沉产子
- 木治
- 木活字
- 木浦 (Mùpǔ)
- 木浦模式
- 木港 (Mùgǎng)
- 木渠芝
- 木漿/木浆
- 木漸/木渐
- 木瀆/木渎
- 木災/木灾
- 木炭 (mùtàn)
- 木炭畫/木炭画 (mùtànhuà)
- 木然 (mùrán)
- 木焦油
- 木煤氣/木煤气
- 木熙
- 木燧
- 木牀
- 木片 (mùpiàn)
- 木版 (mùbǎn)
- 木版印刷
- 木版圖/木版图
- 木版水印
- 木版畫/木版画
- 木牋/木笺
- 木牌 (mùpái)
- 木牒
- 木牘/木牍 (mùdú)
- 木牛
- 木牛流馬/木牛流马 (mùniú liúmǎ)
- 木犀 (mùxī)
- 木狗子
- 木猴而冠
- 木獸/木兽
- 木獺/木獭
- 木王
- 木珊瑚
- 木理
- 木球 (mùqiú)
- 木琴 (mùqín)
- 木瓜 (mùguā)
- 木瓜山
- 木瓜杖
- 木瓜海棠
- 木瓜酵素
- 木瓦 (mùwǎ)
- 木產/木产
- 木甲
- 木畫/木画
- 木癭/木瘿
- 木皇
- 木皮
- 木皮嶺/木皮岭
- 木皮散人
- 木盧/木卢
- 木石 (mùshí)
- 木石心腸/木石心肠
- 木石為徒/木石为徒
- 木硬
- 木硯/木砚
- 木碗
- 木磚/木砖
- 木礱/木砻
- 木祚
- 木神
- 木禺
- 木禺人
- 木禺馬/木禺马
- 木禺龍/木禺龙
- 木禾
- 木稅/木税
- 木稼
- 木稷
- 木突
- 木立 (mùlì)
- 木竹 (mùzhú)
- 木竹子
- 木笏
- 木笏司
- 木符
- 木筆/木笔
- 木筏 (mùfá)
- 木管 (mùguǎn)
- 木管樂器/木管乐器 (mùguǎn yuèqì)
- 木簪
- 木簡/木简 (mùjiǎn)
- 木精 (mùjīng)
- 木紀/木纪
- 木紅毬/木红球
- 木紅色/木红色
- 木索
- 木紋/木纹
- 木紹/木绍
- 木綿/木绵
- 木缽/木钵
- 木罌/木罂
- 木罌缶/木罂缶
- 木罌缻/木罂缻
- 木羽
- 木羽弩箭
- 木老老
- 木老鴉/木老鸦
- 木耦
- 木耳 (mù'ěr)
- 木聖/木圣
- 木聲/木声
- 木胎
- 木胎兒/木胎儿
- 木脈/木脉
- 木腔
- 木腸/木肠
- 木腳客/木脚客
- 木腦殼/木脑壳
- 木腳道/木脚道
- 木膚/木肤
- 木臼
- 木舌
- 木船 (mùchuán)
- 木舶
- 木芍藥/木芍药
- 木芽
- 木芝
- 木花油
- 木芙蓉 (mùfúróng)
- 木茹
- 木莓 (mùméi)
- 木落
- 木葉/木叶 (mùyè)
- 木葉山/木叶山
- 木落歸本/木落归本
- 木葉蝶/木叶蝶
- 木蔥/木葱
- 木蓮/木莲 (mùlián)
- 木蕖
- 木薦/木荐
- 木薯 (mùshǔ)
- 木藍/木蓝
- 木蘭/木兰 (mùlán)
- 木蘭從軍/木兰从军
- 木蘭步/木兰步
- 木蘭舟/木兰舟
- 木蘭船/木兰船
- 木蘭花/木兰花 (mùlánhuā)
- 木處/木处
- 木虻
- 木蜜
- 木螺釘/木螺钉
- 木蟲/木虫
- 木蠟/木蜡
- 木蠹
- 木行
- 木表
- 木製/木制 (mùzhì)
- 木角
- 木觚
- 木解
- 木記/木记
- 木訥/木讷 (mùnè)
- 木訥無言/木讷无言
- 木訥老人/木讷老人
- 木詘/木诎
- 木諫/木谏
- 木變石/木变石
- 木谷
- 木豆
- 木象
- 木貓/木猫
- 木賊/木贼 (mùzéi)
- 木賊草/木贼草
- 木賜/木赐
- 木質/木质 (mùzhì)
- 木質莖/木质茎
- 木質部/木质部 (mùzhìbù)
- 木路
- 木蹻/木跷
- 木車/木车
- 木軨/木𫐉
- 木輅/木辂
- 木造 (mùzào)
- 木通 (mùtōng)
- 木連理/木连理
- 木遁
- 木運/木运
- 木那克
- 木酪
- 木醇
- 木野狐
- 木釐
- 木鉤子/木钩子
- 木錧/木𰾒
- 木錡/木锜
- 木鍾/木钟
- 木鏃/木镞
- 木鐸/木铎
- 木鑣/木镳
- 木鑽/木钻
- 木門/木门
- 木閣/木阁
- 木陛
- 木階/木阶
- 木雁
- 木雍
- 木雕 (mùdiāo)
- 木雕泥塑
- 木雞/木鸡
- 木雞養到/木鸡养到
- 木難/木难 (mùnán)
- 木面雕刻
- 木鞋 (mùxié)
- 木章
- 木頭/木头 (mùtou)
- 木頭人/木头人 (mùtourén)
- 木頭似的/木头似的
- 木頭底兒/木头底儿
- 木頭木腦/木头木脑
- 木頭橛子/木头橛子
- 木食
- 木餳/木饧
- 木餾油/木馏油 (mùliúyóu)
- 木饅頭/木馒头
- 木香 (mùxiāng)
- 木香菊
- 木馬/木马 (mùmǎ)
- 木馬子/木马子
- 木馬計/木马计 (mùmǎjì)
- 木驢/木驴 (mùlǚ)
- 木骨
- 木魅
- 木魚/木鱼 (mùyú)
- 木魚書/木鱼书
- 木魚符/木鱼符
- 木鯨/木鲸
- 木鳶/木鸢
- 木鳳銜書/木凤衔书
- 木鴈
- 木鵝/木鹅
- 木鵰/木雕
- 木鷂/木鹞
- 木鶴/木鹤
- 木鶴仙人/木鹤仙人
- 木鹽/木盐
- 木麻黃/木麻黄
- 木齒/木齿
- 木齒丹/木齿丹
- 木龍/木龙
- 朱木
- 朽木 (xiǔmù)
- 朽木不雕
- 朽木之才
- 朽木死灰
- 朽木生花
- 朽木糞土/朽木粪土
- 朽木糞牆/朽木粪墙 (xiǔmùfènqiáng)
- 朽木蟲/朽木虫
- 朽木難彫/朽木难雕
- 朽株枯木
- 材木 (cáimù)
- 杉木
- 杖頭木偶/杖头木偶
- 果木 (guǒmù)
- 枉木
- 林木 (línmù)
- 枕木 (zhěnmù)
- 松木 (sōngmù)
- 析木
- 枝木之冠
- 松木坪 (Sōngmùpíng)
- 析木津
- 東金西木/东金西木
- 柰何木
- 柴木 (cháimù)
- 枸木
- 柔木
- 柚木
- 柏木 (bǎimù)
- 枯木
- 柘木 (Zhèmù)
- 枹木
- 枯木再生
- 枯木堂
- 枹木履
- 枯木朽株
- 枯木死灰
- 柏木油
- 枯木生花
- 枯木發榮/枯木发荣
- 枯木眾/枯木众
- 柳木腿
- 枯木逢春
- 枯木龍吟/枯木龙吟
- 枯株朽木
- 柴達木河/柴达木河
- 栒子木
- 桀木
- 栯木
- 株木
- 桐木人
- 栗木坑 (Lìmùkēng)
- 桐木布
- 桐木魚/桐木鱼
- 格爾木/格尔木 (Gé'ěrmù)
- 桃花心木 (táohuāxīnmù)
- 梁木
- 桴木
- 梁木其壞
- 梧桐木
- 椋子木
- 椓木
- 棶木/梾木
- 棧木/栈木
- 棗木/枣木
- 森木
- 棺木 (guānmù)
- 棘木之下
- 棘木之聽/棘木之听
- 棠木舫
- 椽木
- 楬木
- 楷木
- 楞木
- 楚木
- 榆木 (yúmù)
- 楠木 (nánmù)
- 楓木/枫木
- 楓木人/枫木人
- 楔木炮
- 榆木炮
- 椿木營/椿木营 (Chūnmùyíng)
- 榆木腦殼/榆木脑壳
- 榆木腦袋/榆木脑袋
- 榣木
- 槃木
- 榮木/荣木
- 榑木
- 槁木
- 榒木
- 構木/构木
- 槃木朽株
- 槁木死灰
- 樠木/𣗊木
- 樚木
- 樛木
- 樹木/树木 (shùmù)
- 樺木/桦木 (huàmù)
- 橫木/横木 (héngmù)
- 橉木
- 樳木/桪木
- 橈木/桡木
- 樸木/朴木
- 橉筋木
- 檑木
- 檠木
- 檜木/桧木
- 檀木靴
- 櫑木
- 櫸木/榉木 (jǔmù)
- 死灰槁木
- 民族蘇木/民族苏木
- 水丑木
- 水木
- 水木匠
- 水木明瑟
- 水木清華/水木清华
- 求魚緣木/求鱼缘木
- 池魚林木/池鱼林木
- 沙木 (shāmù)
- 沈木
- 沈木香
- 泥塑木雕
- 泰山梁木
- 波斯喀木 (Bōsīkāmù)
- 泥木
- 油木梳
- 泥水木作
- 泥水木匠
- 油煔木
- 浪木
- 浮石沉木
- 浮石沈木
- 滾木/滚木
- 潮州木雕
- 灌木 (guànmù)
- 灰木
- 災木/灾木
- 烏文木/乌文木
- 烏木/乌木 (wūmù)
- 烏蘭木倫/乌兰木伦 (Wūlánmùlún)
- 烏魯木齊/乌鲁木齐 (Wūlǔmùqí)
- 無患木/无患木
- 無灰木/无灰木
- 燧木
- 牛山木
- 犢木子/犊木子
- 狗腳木/狗脚木
- 猩猩木 (xīngxīngmù)
- 獨木不林/独木不林
- 獨木橋/独木桥 (dúmùqiáo)
- 獨木舟/独木舟 (dúmùzhōu)
- 獨木船/独木船
- 獨木難支/独木难支
- 玄木
- 珍木
- 瑞木
- 瑤木/瑶木
- 瑰木
- 瓔珞木/璎珞木
- 甘木 (Gānmù)
- 生木
- 異木/异木
- 異木奇花/异木奇花
- 畫地刻木/画地刻木
- 番木瓜 (fānmùguā)
- 番木鱉/番木鳖
- 痲木/痳木
- 瘣木
- 癭木/瘿木
- 發木/发木
- 登木
- 登木求魚/登木求鱼
- 白塞木
- 白木
- 白木耳 (báimù'ěr)
- 百木
- 百木長/百木长
- 皇木
- 盜木/盗木
- 直木必伐
- 直木賞/直木赏
- 相思木
- 睿木
- 石心木腸/石心木肠
- 石鹽木/石盐木
- 砍木
- 破土斷木/破土断木
- 砧木
- 硬木 (yìngmù)
- 社木
- 社木砦/社木寨
- 神木 (shénmù)
- 神木愣吞
- 禾木旁 (hémùpáng)
- 秀木
- 秋木
- 移木之信
- 移花接木 (yíhuājiēmù)
- 稠木
- 積木/积木 (jīmù)
- 空木
- 窬木
- 窮猿失木/穷猿失木
- 窾木
- 竅木/窍木
- 立木
- 童木
- 端木 (Duānmù)
- 竹木 (zhúmù)
- 竹頭木屑/竹头木屑
- 竻木
- 竿木
- 竿木逢場/竿木逢场
- 節木鳥/节木鸟
- 紅木/红木 (hóngmù)
- 素木
- 紋木/纹木
- 素木床
- 納木那尼/纳木那尼 (Nàmù Nàní)
- 綟木/𫄫木
- 緣木/缘木
- 緣木希魚/缘木希鱼
- 緣木求魚/缘木求鱼 (yuánmùqiúyú)
- 繁木
- 繩木/绳木
- 繩鋸木斷/绳锯木断
- 罄山採木/罄山采木
- 聖木/圣木
- 聲振林木/声振林木
- 聲風木/声风木
- 肋木
- 肝木
- 胡桃木
- 腐木
- 膠木/胶木 (jiāomù)
- 良禽擇木/良禽择木 (liángqínzémù)
- 花木
- 花木扶疏
- 花木瓜
- 花木蘭/花木兰
- 花櫚木/花榈木
- 若木 (ruòmù)
- 苞木
- 苗木 (miáomù)
- 草木 (cǎomù)
- 草木樨 (cǎomùxī)
- 草木灰 (cǎomùhuī)
- 草木皆兵 (cǎomùjiēbīng)
- 草木知威
- 草木驚心/草木惊心
- 草衣木食
- 落木 (luòmù)
- 蓋孜庫木/盖孜库木 (Gàizīkùmù)
- 蘇木/苏木 (sūmù)
- 蘿芙木/萝芙木 (luófúmù)
- 蚊子木
- 蚊母木
- 蛇木
- 蜆木/蚬木
- 蜚瓦拔木
- 蟠木
- 蟠木朽株
- 蠢若木雞/蠢若木鸡
- 蠹木
- 行將就木/行将就木 (xíngjiāngjiùmù)
- 行木
- 衡木
- 表木
- 被赭貫木/被赭贯木
- 觚木
- 觸石決木/触石决木
- 誹謗之木/诽谤之木
- 謗木/谤木
- 讓木/让木
- 象牙木
- 貞木/贞木
- 貫木/贯木
- 質木/质木
- 賽里木 (Sàilǐmù)
- 贅木/赘木
- 踢木
- 踏混木
- 踏滾木/踏滚木
- 蹶石伐木
- 身非木石
- 車梁木
- 軟木/软木 (ruǎnmù)
- 軟木塞/软木塞 (ruǎnmùsāi)
- 軟木畫/软木画
- 軟木磚/软木砖
- 軟硬木/软硬木
- 輅木/辂木
- 逢場竿木/逢场竿木
- 連木/连木
- 連理木/连理木
- 通脫木/通脱木
- 通香木
- 連齒木屐/连齿木屐
- 道木 (dàomù)
- 過木梳/过木梳
- 邪木
- 郭勒木德 (Guōlèmùdé)
- 醉木犀
- 醒木
- 重陽木/重阳木
- 野木
- 金口木舌
- 金木
- 金木犀
- 銜木/衔木
- 銜木鳥/衔木鸟
- 鋟木/锓木
- 鐵力木/铁力木
- 鐵心木腸/铁心木肠
- 鐵木/铁木
- 鐵木真/铁木真 (Tiěmùzhēn)
- 鐵木里克 (Tiěmùlǐkè)
- 鐵熱木/铁热木 (Tiěrèmù)
- 鐵線木偶/铁线木偶
- 鐵腳木鵝/铁脚木鹅
- 鑄木鏤冰/铸木镂冰
- 鑲銅木鞋/镶铜木鞋
- 鑽木/钻木
- 鑽木取火/钻木取火 (zuānmùqǔhuǒ)
- 鑽木得火/钻木得火
- 關木/关木
- 阿拉木汗
- 阿木忽郎
- 阿木林 (āmùlín)
- 阿洪魯庫木/阿洪鲁库木 (Āhóng Lǔkùmù)
- 陰木/阴木
- 陵木
- 陰沉木/阴沉木
- 陽木/阳木
- 雜木/杂木
- 雨木冰
- 雲木/云木
- 電木/电木 (diànmù)
- 霜木
- 露木
- 霹靂木/霹雳木
- 靈木/灵木
- 青木 (Qīngmù)
- 青木香
- 青黃溝木/青黄沟木
- 面如槁木
- 革木
- 韓朋木/韩朋木
- 類木行星/类木行星
- 風木/风木
- 風木之思/风木之思
- 風木之悲/风木之悲
- 風木含悲/风木含悲
- 風木歎/风木叹
- 飲木/饮木
- 香木 (xiāngmù)
- 香楠木
- 香羅木/香罗木
- 馬醉木/马醉木 (mǎzuìmù)
- 驚堂木/惊堂木 (jīngtángmù)
- 鬼木
- 鬼木串
- 魚木/鱼木
- 魚緣木/鱼缘木
- 鳴于喬木/鸣于乔木
- 鳳凰木/凤凰木 (fènghuángmù)
- 鳴雁直木/鸣雁直木
- 鷹架木/鹰架木
- 鸂鶒木/㶉𫛶木
- 鹽膚木/盐肤木
- 麗木/丽木
- 麵木/面木
- 麻木 (mámù)
- 麻木不仁 (mámùbùrén)
- 黃木/黄木
- 黃櫨木/黄栌木
- 黃蘆木/黄芦木
- 黃連木/黄连木 (huángliánmù)
- 黑木耳 (hēimù'ěr)
- 黑檀木 (hēitánmù)
- 龍木/龙木
- 龍骨木/龙骨木
Descendants[edit]
Other:
- → Lü: ᦙᦴᧉ (muu²)
Japanese[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Readings[edit]
- Go-on: もく (moku, Jōyō)
- Kan-on: ぼく (boku, Jōyō)
- Kun: き (ki, 木, Jōyō); こ (ko, 木, Jōyō †)
- Nanori: ぐ (gu); しげ (shige); も (mo); もと (moto)
Etymology 1[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 木 |
| き Grade: 1 |
| kun’yomi |
| Alternative spelling |
|---|
| 樹 (uncommon) |
⟨ki2⟩ → */kɨ/ → /ki/
From Old Japanese 木 (ki2), from Proto-Japonic *kəy. Cognate with Proto-Ryukyuan *ke. For the vowel alternation, see Wiktionary:About Proto-Japonic § Standalone forms and combining forms.
First attested in the Kojiki of 712 CE.[1]
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
- a tree or shrub
- wood, timber, lumber
- (graph theory, computer science) a tree (data structure)
- (theater, sumo, etc.) a clapper used to signal the opening or closing of a match or play
Idioms[edit]
- 猿も木から落ちる (saru mo ki kara ochiru, “even monkeys fall from trees → nobody's perfect”)
Etymology 2[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 木 |
| こ Grade: 1 |
| kun’yomi |
⟨ko2⟩ → */kə/ → /ko/
From Old Japanese 木 (ko2).
Likely the original form of ki above. Obsolete in modern Japanese, never found in isolation; only found in compounds and certain idioms.[3]
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
Derived terms[edit]
Etymology 3[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 木 |
| もく Grade: 1 |
| goon |
From Middle Chinese 木 (MC muwk). The 呉音 (goon, literally “Wu sound”) reading, so likely the original borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Compare modern Cantonese 木 (muk6).
Alternative forms[edit]
- (wood grain): 杢
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
Derived terms[edit]
Etymology 4[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 木 |
| ぼく Grade: 1 |
| kan’on |
From Middle Chinese 木 (MC muwk). The 漢音 (kan'on, literally “Han sound”) reading, so likely a later borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Compare literary Min Nan 木 (bo̍k).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
- a tree; more specifically, a living tree
- the bent and gnarled trunk or roots of an old tree
- wood, lumber
- something made of wood
- in ancient China, a wooden musical instrument
Adjective[edit]
木 • (boku) -na (adnominal 木な (boku na), adverbial 木に (boku ni))
- (derogatory) wooden, as of a person's character or behavior
- (derogatory) wooden, as of a person's mental abilities: blockheaded, stupid, dimwitted
Inflection[edit]
| Stem forms | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Imperfective (未然形) | 木だろ | ぼくだろ | boku daro |
| Continuative (連用形) | 木で | ぼくで | boku de |
| Terminal (終止形) | 木だ | ぼくだ | boku da |
| Attributive (連体形) | 木な | ぼくな | boku na |
| Hypothetical (仮定形) | 木なら | ぼくなら | boku nara |
| Imperative (命令形) | 木であれ | ぼくであれ | boku de are |
| Key constructions | |||
| Informal negative | 木ではない 木じゃない |
ぼくではない ぼくじゃない |
boku de wa nai boku ja nai |
| Informal past | 木だった | ぼくだった | boku datta |
| Informal negative past | 木ではなかった 木じゃなかった |
ぼくではなかった ぼくじゃなかった |
boku de wa nakatta boku ja nakatta |
| Formal | 木です | ぼくです | boku desu |
| Formal negative | 木ではありません 木じゃありません |
ぼくではありません ぼくじゃありません |
boku de wa arimasen boku ja arimasen |
| Formal past | 木でした | ぼくでした | boku deshita |
| Formal negative past | 木ではありませんでした 木じゃありませんでした |
ぼくではありませんでした ぼくじゃありませんでした |
boku de wa arimasen deshita boku ja arimasen deshita |
| Conjunctive | 木で | ぼくで | boku de |
| Conditional | 木なら(ば) | ぼくなら(ば) | boku nara (ba) |
| Provisional | 木だったら | ぼくだったら | boku dattara |
| Volitional | 木だろう | ぼくだろう | boku darō |
| Adverbial | 木に | ぼくに | boku ni |
| Degree | 木さ | ぼくさ | bokusa |
References[edit]
- ^ “木・樹”, in 日本国語大辞典 (Nihon Kokugo Daijiten, “Nihon Kokugo Daijiten”)[1] (in Japanese), concise edition, Tōkyō: Shogakukan, 2000
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 (in Japanese), Third edition, Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ^ Pellard, Thomas (2012) “日琉祖語の分岐年代”, in 琉球諸語と古代日本語に関する比較言語学的研究」ワークショップ[2], page 6
Korean[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Middle Chinese 木 (MC muwk).
| Historical Readings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dongguk Jeongun Reading | ||
| Dongguk Jeongun, 1448 | 목〮 (Yale: mwók) | |
| Middle Korean | ||
| Text | Eumhun | |
| Gloss (hun) | Reading | |
| Hunmong Jahoe, 1527[5] | 나모 (Yale: nàmwò) | 목〮 (Yale: mwók) |
Pronunciation[edit]
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [mo̞k̚]
- Phonetic hangul: [목]
Hanja[edit]
- Hanja form? of 목 (“tree; wood; wooden”). [affix]
- Hanja form? of 목 (“Short for 목요일(木曜日) (mogyoil, “Thursday”).”).
Compounds[edit]
- 각목 (刻木, gangmok)
- 고목 (古木, gomok)
- 관목 (灌木, gwanmok)
- 광목 (廣木, gwangmok)
- 교목 (喬木, gyomok)
- 모과 (木瓜, mogwa)
- 목간 (木簡, mokgan)
- 목검 (木劍, mokgeom)
- 목공 (木工, mokgong)
- 목관 (木管, mokgwan)
- 목기 (木器, mokgi)
- 목도 (木刀, mokdo)
- 목련 (木蓮, mongnyeon)
- 목마 (木馬, mongma)
- 목석 (木石, mokseok)
- 목성 (木星, mokseong)
- 목수 (木手, moksu)
- 목어 (木魚, mogeo)
- 목재 (木材, mokjae)
- 목조 (木造, mokjo)
- 목조 (木彫, mokjo)
- 목초 (木醋, mokcho)
- 목침 (木枕, mokchim)
- 목탁 (木鐸, moktak)
- 목탄 (木炭, moktan)
- 목탑 (木塔, moktap)
- 목화 (木花, mokhwa)
- 묘목 (苗木, myomok)
- 벌목 (伐木, beolmok)
- 비목 (碑木, bimok)
- 삽목 (揷木, sammok)
- 수목 (樹木, sumok)
- 식목 (植木, singmok)
- 신목 (神木, sinmok)
- 원목 (原木, wonmok)
- 접목 (接木, jeommok)
- 주목 (朱木, jumok)
- 취목 (取木, chwimok)
- 침목 (枕木, chimmok)
References[edit]
- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [6]
Okinawan[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Readings[edit]
Etymology[edit]
/ki/ → /kiː/
From Proto-Ryukyuan *ke, from Proto-Japonic *kəy.
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
木 (kī)
- a tree
References[edit]
- “キー(きー)” in Okinawan Dialect Dictionary - Ajima.
Old Japanese[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
From Proto-Japonic *kəy.
This term had then came to be used as 借訓 (shakkun) kanji for ki2.
Noun[edit]
木 (ki2) (kana き)
Phonogram[edit]
木 (ki2)
- Denotes phonographic syllable ki2.
Descendants[edit]
- Japanese: 木 (ki)
Etymology 2[edit]
Likely the original form of ⟨ki2⟩ above. Never found in isolation.[1]
Noun[edit]
木 (ko2) (kana こ)
- Combining form of キ乙 (ki2) above
Derived terms[edit]
Descendants[edit]
- Japanese: 木 (ko)
Etymology 3[edit]
May ultimately be from Proto-Japonic *kəy. Analysis in the Nihon Shoki (720 CE) shows that this variation of ⟨ki2⟩ is not limited to Eastern dialects.
Noun[edit]
木 (ke2) (kana け)
- (regional, Northern Eastern Old Japanese, Southern Eastern Old Japanese) Same as キ乙 (ki2) above
- , text here
- 麻都能氣乃奈美多流美礼波伊波妣等乃和例乎美於久流等多多理之母己呂
- matu no2 ke2 no2 nami1taru mi1reba ipabi1to2 no2 ware wo mi1okuru to2 tatari si moko2ro2
- Looking at the pine trees all in a row, they were just like the people from the household standing to see me off
- , text here
Derived terms[edit]
References[edit]
Vietnamese[edit]
Han character[edit]
木: Hán Việt readings: mộc (
木: Nôm readings: mọc[1][2][3][4][5], mốc[1][2][3][4][5], mộc[1][2][3][5], móc[1][3][4][5], mục[3][4][5], chúc[2]
Compounds[edit]
References[edit]
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han pictograms
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Chinese adjectives
- Mandarin adjectives
- Dungan adjectives
- Cantonese adjectives
- Taishanese adjectives
- Gan adjectives
- Hakka adjectives
- Jin adjectives
- Northern Min adjectives
- Eastern Min adjectives
- Hokkien adjectives
- Teochew adjectives
- Wu adjectives
- Xiang adjectives
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese Han characters
- Mandarin terms with collocations
- Literary Chinese terms with quotations
- Chinese nouns classified by 條/条
- Chinese nouns classified by 塊/块
- Chinese nouns classified by 嚿
- Chinese nouns classified by 轆/辘
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese literary terms
- Chinese surnames
- Mandarin Chinese
- Chinese neologisms
- Chinese slang
- Chinese eye dialect
- Elementary Mandarin
- zh:Plants
- Japanese Han characters
- Grade 1 kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading もく
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading ぼく
- Japanese kanji with kun reading き
- Japanese kanji with kun reading こ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ぐ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading しげ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading も
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading もと
- Japanese terms spelled with 木 read as き
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms written with one Han script character
- Japanese terms spelled with 木
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- ja:Graph theory
- ja:Computer science
- ja:Theater
- ja:Sumo
- Japanese terms spelled with 木 read as こ
- Japanese terms spelled with 木 read as もく
- Japanese terms read with on'yomi
- Japanese terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Japanese short forms
- Japanese terms spelled with 木 read as ぼく
- Japanese adjectives
- Japanese な-na adjectives
- Japanese derogatory terms
- ja:Plants
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Korean lemmas
- Korean Han characters
- ko:Days of the week
- Okinawan Han characters
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading きー
- Okinawan kanji with kun readings missing okurigana designation
- Okinawan terms inherited from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Okinawan terms derived from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Okinawan terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Okinawan terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Okinawan terms with IPA pronunciation
- Okinawan lemmas
- Okinawan nouns
- Okinawan terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Okinawan terms written with one Han script character
- Okinawan terms spelled with 木
- Okinawan single-kanji terms
- ryu:Plants
- Old Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Old Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Old Japanese lemmas
- Old Japanese nouns
- Old Japanese phonograms
- Regional Old Japanese
- Old Japanese terms with usage examples
- ojp:Plants
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom
- CJKV radicals

