石
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual[edit]
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character[edit]
石 (Kangxi radical 112, 石+0, 5 strokes, cangjie input 一口 (MR), four-corner 10600, composition ⿸丆口)
- Kangxi radical #112, ⽯.
Derived characters[edit]
- Appendix:Chinese radical/石
- 佦, 㓈, 𠰴, 坧, 妬, 𡯝, 𡶌, 𫹺, 拓, 沰, 𨒙, 𪰒, 柘, 𣭏, 炻, 𤤟, 𦚈, 祏, 䄷, 䇉, 袥, 𫂹, 䖨, 𧣔, 𧦳, 磊, 䞠, 跖, 𨋓, 鉐(𬬷), 鮖, 鼫, 𮯂
- 劯, 斫, 𣗁, 䲽, 宕, 岩, 沯, 𥥔, 𫅂, 雼, 𡻦, 𮫁, 𪔑, 𪊞, 𭚇, 乭, 𭀽, 𡊵, 𡶪, 𤇈, 㸴, 𧵔, 𨀂, 𨥴, 䦒, 𡇈, 唘, 䀾, 㻹, 𥗉, 𥗌, 𥗐, 𥗑, 𥗹, 𥗺, 𥗻, 𥗼, 𥗽, 𥗾, 𥗿, 𥘀, 𥘁, 𥘂, 𥘃, 𥘄
References[edit]
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 827, character 1
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 24024
- Dae Jaweon: page 1239, character 7
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 4, page 2416, character 1
- Unihan data for U+77F3
Chinese[edit]
| simp. and trad. |
石 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin[edit]
| Historical forms of the character 石 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|
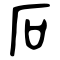
|

|

|

|
Pictogram (象形) : a stone beneath a cliff (厂). The cliff was subsequently distorted into 丆.
Alternatively, a cave set into the side of a cliff or mountain.
Etymology 1[edit]
Unknown. Probably related to Proto-Vietic *l-taːʔ (“stone”) (whence Vietnamese đá and Khmer ដា (daa, “rock; stone”)) (Schuessler, 2007), to which Chinese would have added the familiar final -k.
Pronunciation[edit]
Definitions[edit]
石
Synonyms[edit]
Compounds[edit]
- 一片石
- 三生石
- 下石
- 上馬石/上马石
- 亂石/乱石 (luànshí)
- 介石
- 信石 (xìnshí)
- 光鹵石/光卤石
- 八石
- 凍石/冻石
- 凝水石
- 刊石
- 刻石 (kèshí)
- 剛石/刚石
- 勒石 (lèshí)
- 化石 (huàshí)
- 化石學/化石学
- 匠石 (jiàngshí)
- 匪石
- 印石
- 卵石 (luǎnshí)
- 古石 (Gǔshí)
- 吐酒石
- 吸鐵石/吸铁石 (xītiěshí)
- 嘛呢石 (mānīshí)
- 嘉石
- 土石 (tǔshí)
- 土石流 (tǔshíliú)
- 基石 (jīshí)
- 培石 (Péishí)
- 墊腳石/垫脚石 (diànjiǎoshí)
- 壽山石/寿山石
- 大理石 (dàlǐshí)
- 太湖石
- 太石 (Tàishí)
- 天青石 (tiānqīngshí)
- 孔雀石 (kǒngquèshí)
- 安石榴 (ānshíliú)
- 寶石/宝石 (bǎoshí)
- 寶石婚/宝石婚
- 尖石 (Jiānshí)
- 岩石 (yánshí)
- 岩石圈 (yánshíquān)
- 岩石學/岩石学 (yánshíxué)
- 嵌石
- 巖石/岩石 (yánshí)
- 巨石
- 忍石
- 怪石
- 慈石
- 戒石
- 打火石 (dǎhuǒshí)
- 採石場/采石场 (cǎishíchǎng)
- 撇火石
- 擲石子/掷石子
- 文石
- 斜長石/斜长石 (xiéchángshí)
- 方解石 (fāngjiěshí)
- 旋石
- 昌化石 (chānghuàshí)
- 明石 (míngshí)
- 月石
- 月長石/月长石 (yuèchángshí)
- 望夫石 (wàngfūshí)
- 木化石
- 木石 (mùshí)
- 木變石/木变石
- 東石/东石 (Dōngshí)
- 松脂石
- 柱石 (zhùshí)
- 氟石 (fúshí)
- 水刷石
- 水滴石穿 (shuǐdīshíchuān)
- 水磨石
- 河卵石
- 油石
- 泉石 (quánshí)
- 泥石流 (níshíliú)
- 活化石 (huóhuàshí)
- 洗石
- 海泡石
- 消石灰 (xiāoshíhuī)
- 海綠石/海绿石
- 海花石
- 湖山石
- 滑石 (huáshí)
- 滑石粉 (huáshífěn)
- 滴石
- 瀝青石/沥青石
- 火石 (huǒshí)
- 灰石
- 烏心石/乌心石
- 熟石灰 (shúshíhuī)
- 熟石膏
- 燒石膏/烧石膏
- 燧石 (suìshí)
- 爐甘石/炉甘石 (lúgānshí)
- 牙結石/牙结石
- 玄石
- 玉石 (yùshí)
- 璇石 (soān-chio̍h) (Min Nan)
- 瓦石峽/瓦石峡 (Wǎshíxiá)
- 生石灰 (shēngshíhuī)
- 生石膏
- 界石 (jièshí)
- 畫像石/画像石 (huàxiàngshí)
- 番石榴 (fānshíliú)
- 發石車/发石车
- 白信石
- 白石坳 (Báishí'ào)
- 白石神
- 白雲石/白云石 (báiyúnshí)
- 皂石 (zàoshí)
- 盤石/盘石 (pánshí)
- 盤陀石/盘陀石
- 矢石 (shǐshí)
- 石井 (Shíjǐng)
- 石交
- 石人
- 石像 (shíxiàng)
- 石刀
- 石刁柏 (shídiāobǎi)
- 石刻 (shíkè)
- 石包城 (Shíbāochéng)
- 石化 (shíhuà)
- 石匠
- 石南
- 石印
- 石印本
- 石卵 (shíluǎn)
- 石友
- 石器 (shíqì)
- 石器時代/石器时代 (Shíqì Shídài)
- 石坎
- 石埠 (Shíbù)
- 石塊/石块 (shíkuài)
- 石墩 (shídūn)
- 石壁 (shíbì)
- 石女 (shínǚ)
- 石女山 (Shínǚshān)
- 石婦/石妇
- 石子 (shízǐ)
- 石子兒/石子儿 (shízǐr)
- 石室 (shíshì)
- 石家莊/石家庄 (Shíjiāzhuāng)
- 石尤風/石尤风
- 石屋頭/石屋头 (Shíwūtóu)
- 石山 (Shíshān)
- 石岐 (Shíqí)
- 石工 (shígōng)
- 石幢
- 石床
- 石擔/石担 (shídàn)
- 石敢當/石敢当 (shígǎndāng)
- 石文
- 石斑魚/石斑鱼 (shíbānyú)
- 石料 (shíliào)
- 石斛 (shíhú)
- 石斛蘭/石斛兰
- 石斧
- 石方 (shífāng)
- 石晉/石晋 (Shíjìn)
- 石本 (shíběn)
- 石材 (shícái)
- 石林 (shílín)
- 石松
- 石板 (shíbǎn)
- 石板巷 (Shíbǎnxiàng)
- 石柱 (shízhù)
- 石梁河 (Shíliánghé)
- 石棺 (shíguān)
- 石棉 (shímián)
- 石棉瓦
- 石棉症
- 石榴 (shíliú)
- 石榴裙 (shíliúqún)
- 石橋/石桥 (shíqiáo)
- 石橋驛/石桥驿 (Shíqiáoyì)
- 石民
- 石沉大海 (shíchéndàhǎi)
- 石決明/石决明 (shíjuémíng)
- 石泉
- 石油 (shíyóu)
- 石油氣/石油气 (shíyóuqì)
- 石油腦/石油脑
- 石油蕉
- 石洞 (Shídòng)
- 石渠 (Shíqú)
- 石滬/石沪
- 石灘/石滩 (shítān)
- 石火 (shíhuǒ)
- 石灰 (shíhuī)
- 石灰乳
- 石灰岩 (shíhuīyán)
- 石灰水 (shíhuīshuǐ)
- 石灰石 (shíhuīshí)
- 石灰窯/石灰窑 (Shíhuīyáo)
- 石灰質/石灰质
- 石炭 (shítàn)
- 石炭紀/石炭纪 (Shítàn Jì)
- 石燕
- 石牆/石墙 (shíqiáng)
- 石版 (shíbǎn)
- 石版屋
- 石版畫/石版画
- 石版石
- 石版路
- 石牌 (Shípái)
- 石牛道
- 石獅子/石狮子 (shíshīzi)
- 石田 (shítián)
- 石盤/石盘 (Shípán)
- 石破天驚/石破天惊 (shípòtiānjīng)
- 石硯/石砚
- 石碇 (shídìng)
- 石碑 (shíbēi)
- 石碣
- 石磧/石碛 (Shíqì)
- 石磨 (shímò)
- 石磴
- 石礫/石砾
- 石窟 (shíkū)
- 石竹 (shízhú)
- 石筍/石笋 (shísǔn)
- 石筆/石笔
- 石級/石级 (shíjí)
- 石絨/石绒
- 石經/石经 (shíjīng)
- 石綿/石绵 (shímián)
- 石綠/石绿
- 石羊
- 石耳 (shí'ěr)
- 石胡荽 (shíhúsuī)
- 石脂
- 石膏 (shígāo)
- 石膏像
- 石舫 (shífǎng)
- 石花 (shíhuā)
- 石花菜 (shíhuācài)
- 石英 (shíyīng)
- 石英岩
- 石英錶/石英表
- 石英鐘/石英钟 (shíyīngzhōng)
- 石菖蒲 (shíchāngpú)
- 石蒜
- 石蓮/石莲
- 石蕊 (shíruǐ)
- 石蘭/石兰
- 石蟥
- 石蠟/石蜡 (shílà)
- 石蠶/石蚕
- 石製/石制
- 石象 (shíxiàng)
- 石針/石针
- 石鐘乳/石钟乳
- 石門/石门 (shímén)
- 石階/石阶 (shíjiē)
- 石雕
- 石青
- 石韋/石韦 (shíwěi)
- 石頭/石头 (shítou)
- 石頭兒/石头儿
- 石頭城/石头城
- 石頭草/石头草
- 石頭記/石头记
- 石頭餅/石头饼
- 石首 (shíshǒu)
- 石首魚/石首鱼 (shíshǒuyú)
- 石鱉/石鳖
- 石鹼/石碱 (shíjiǎn)
- 石墨 (shímò)
- 石黛 (shídài)
- 石點頭/石点头
- 石鼓 (shígǔ)
- 石鼓文 (shígǔwén)
- 石龍/石龙 (Shílóng)
- 石龍子/石龙子 (shílóngzǐ)
- 石龍芻/石龙刍
- 矽線石/矽线石
- 砂石 (shāshí)
- 砂石場/砂石场
- 砂石車/砂石车
- 砭石 (biānshí)
- 硝石 (xiāoshí)
- 硬石膏 (yìngshígāo)
- 碇石
- 碑石 (bēishí)
- 碎石 (suìshí)
- 磁石 (císhí)
- 磐石 (pánshí)
- 磨刀石 (módāoshí)
- 磨石 (móshí)
- 磷灰石 (línhuīshí)
- 礁石 (jiāoshí)
- 礌石 (léishí)
- 礞石 (méngshí)
- 礫石/砾石 (lìshí)
- 礬石/矾石 (fánshí)
- 礦石/矿石 (kuàngshí)
- 秋石 (qiūshí)
- 秦刻石
- 穹石
- 端石
- 箴石
- 箭石
- 紅信石/红信石
- 紅寶石/红宝石 (hóngbǎoshí)
- 細石器/细石器 (xìshíqì)
- 紫石英 (zǐshíyīng)
- 絆腳石/绊脚石 (bànjiǎoshí)
- 結石/结石 (jiéshí)
- 經石峪/经石峪
- 綠寶石/绿宝石 (lǜbǎoshí)
- 綠松石/绿松石 (lǜsōngshí)
- 綠柱石/绿柱石 (lǜzhùshí)
- 綠泥石/绿泥石
- 羊背石
- 耳石 (ěrshí)
- 肺石
- 腎結石/肾结石 (shènjiéshí)
- 膽石/胆石 (dǎnshí)
- 膽結石/胆结石 (dǎnjiéshí)
- 花崗石/花岗石 (huāgāngshí)
- 花石綱/花石纲
- 英石
- 草石蠶/草石蚕
- 菊石
- 落石 (luòshí)
- 葉蠟石/叶蜡石
- 藍寶石/蓝宝石 (lánbǎoshí)
- 藍晶石/蓝晶石
- 藥石/药石 (yàoshí)
- 蘭石/兰石
- 虎眼石 (hǔyǎnshí)
- 蛇紋石/蛇纹石 (shéwénshí)
- 蛭石 (zhìshí)
- 螢石/萤石 (yíngshí)
- 衡石
- 補腎石/补肾石
- 試金石/试金石 (shìjīnshí)
- 貓眼石/猫眼石
- 貞女石/贞女石
- 貞石/贞石
- 賁石/贲石
- 赤石
- 赤石脂 (chìshízhī)
- 赭石 (zhěshí)
- 踐石/践石
- 踏腳石/踏脚石
- 輝石/辉石 (huīshí)
- 逃石
- 酒石酸 (jiǔshísuān)
- 醒酒石
- 采石磯/采石矶
- 重晶石 (zhòngjīngshí)
- 金剛石/金刚石 (jīngāngshí)
- 金瓜石
- 金石 (jīnshí)
- 金石交
- 金石例
- 金石奏
- 金石學/金石学 (jīnshíxué)
- 金石文
- 金石索
- 金石聲/金石声
- 金石語/金石语
- 金石錄/金石录
- 金紅石/金红石 (jīnhóngshí)
- 釷石/钍石
- 鋪路石/铺路石
- 鋰輝石/锂辉石 (lǐhuīshí)
- 錫石/锡石 (xīshí)
- 鍮石/𨱎石
- 鐘乳石/钟乳石 (zhōngrǔshí)
- 鐵石人/铁石人
- 鐵石心腸/铁石心肠 (tiěshíxīncháng)
- 鑽石/钻石 (zuànshí)
- 鑽石婚/钻石婚
- 長石/长石 (chángshí)
- 陶石
- 陽起石/阳起石 (yángqǐshí)
- 隕石/陨石 (yǔnshí)
- 雞冠石/鸡冠石
- 雙石頭/双石头
- 雞血石/鸡血石
- 離石/离石 (Líshí)
- 雨花石
- 雲石/云石 (yúnshí)
- 電石/电石 (diànshí)
- 電石燈/电石灯
- 霞石 (xiáshí)
- 青田石
- 頑石/顽石 (wánshí)
- 頭頂石/头顶石 (Tóudǐngshí)
- 飛石/飞石 (fēishí)
- 魔法石
- 魚石脂/鱼石脂
- 鵝卵石/鹅卵石 (éluǎnshí)
- 黃石/黄石 (Huángshí)
- 黃石公/黄石公 (Huángshígōng)
- 黃石港/黄石港 (Huángshígǎng)
- 點石成金/点石成金 (diǎnshíchéngjīn)
- 黳石
- 齒石/齿石
Descendants[edit]
(Others)
- → Tocharian B: cāk
Etymology 2[edit]
Contains pronunciations from 擔/担 (dàn) (Qiu, 1988, p. 220).
Pronunciation[edit]
Definitions[edit]
石
Compounds[edit]
References[edit]
- “石”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[1], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Readings[edit]
- Go-on: じゃく (jaku)←じやく (zyaku, historical)
- Kan-on: せき (seki, Jōyō)
- Tō-on: しく (shiku)
- Kan’yō-on: こく (koku, Jōyō †); しゃく (shaku, Jōyō †)←しやく (syaku, historical)
- Kun: いし (ishi, 石, Jōyō); いわ (iwa)←いは (ifa, historical)
- Nanori: あつ (atsu); いさ (isa); いす (isu); いそ (iso); かた (kata); し (shi); せっく (sekku); と (to)
Compounds[edit]
- 標石 (hyōseki, “markstone”)
- 石南花 (shakunage), 石楠花 (shakunage)
- 石英 (sekiei, “quartz; crystal”)
- 石菖 (sekishō, “Japanese sweet flag”)
- 石製 (sekisei, “stonen”)
- 石炭 (sekitan, “coal”)
- 石板 (sekiban, “slate”)
- 石版 (sekiban, “lithograph”)
- 石盤 (sekiban, “slate”)
- 石油 (sekiyu, “oil, petroleum”)
- 石灰 (sekkai, “lime (mineral), quicklime, caustic lime”)
- 石棺 (sekkan, “sarcophagus; stone coffin”)
- 懐石 (kaiseki, “simple meal eaten before tea is served”)
- 化石 (kaseki, “fossil, fossil remains; petrifaction, fossilisation”)
- 岩石 (ganseki, “rock”)
- 奇石 (kiseki, “rare stone; precious gem”)
- 輝石 (kiseki, “pyroxene, augite”)
- 金剛石 (kongōseki, “diamond”)
- 歯石 (shiseki, “dental calculus, tartar”)
- 硝石 (shōseki, “saltpetre”)
- 聖石 (seiseki, “holy stone, rock or mineral”)
- 胆石 (tanseki, “gallstones”)
- 宝石 (hōseki, “gemstone”)
- 木石 (bokuseki, “trees and stones”)
- 石蓴 (aosa, “sea lettuce”)
- 石見 (Iwami)
- 流石 (sasuga)
Etymology 1[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 石 |
| いし Grade: 1 |
| kun’yomi |
⟨isi⟩ → /iɕi/
From Old Japanese.[1] First cited in the Man'yōshū of 759. In turn, the Old Japanese is reconstructed as from Proto-Japonic *esoy.
Likely cognate with 磯 (iso, “pebble; gravel; rocky beach”).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
- a stone
- 1999 March 27, “ストーン・アルマジラー [Stone Armadiller]”, in Vol.2, Konami:
- 体が石のように堅い毛で覆われており、守りがかたい。
- Karada ga ishi no yō ni katai ke de ōwareteori, mamori ga katai.
- With a body covered in a coat as hard as stones, its defence is solid.
- 体が石のように堅い毛で覆われており、守りがかたい。
- (slang, electronics) a transistor
Derived terms[edit]
Etymology 2[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 石 |
| こく Grade: 1 |
| kan’yōon |
From Middle Chinese 斛 (MC huwk).
The 石 spelling came about through customary use in Japan of this character for the unit of measure.[1]
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
- a traditional Japanese unit of volume:
- a unit of quantity for 鮭 (sake, “salmon”) and 鱒 (masu, “trout”); one koku is equal to 40 salmon or 60 trout
Derived terms[edit]
Descendants[edit]
Etymology 3[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 石 |
| せき Grade: 1 |
| kan’on |
From Middle Chinese 石 (MC dzyek).
Pronunciation[edit]
Counter[edit]
- counter for gemstones used as bearings in watches and other devices
- (slang, electronics) counter for transistors, especially discrete ones
- 六石ラジオ
- rokuseki rajio
- six-transistor radio
- 六石ラジオ
Noun[edit]
- Same as こく (koku) above
Affix[edit]
- stone
- needle made of stone
- go stone
- something solid but worthless
- Short for 石見国 (Iwami-no-kuni): Iwami Province
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shōgaku Tosho (1988) 国語大辞典(新装版) [Unabridged Dictionary of Japanese (Revised Edition)] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 (in Japanese), Third edition, Tōkyō: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ^ NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK Publishing, →ISBN
Korean[edit]
Etymology[edit]
From Middle Chinese 石 (MC dzyek).
| Historical Readings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dongguk Jeongun Reading | ||
| Dongguk Jeongun, 1448 | 쎡〮 (Yale: ssyék) | |
| Middle Korean | ||
| Text | Eumhun | |
| Gloss (hun) | Reading | |
| Hunmong Jahoe, 1527[2] | 돌〯 (Yale: twǒl) | 셕〮 (Yale: syék) |
Pronunciation[edit]
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [sʰʌ̹k̚]
- Phonetic hangul: [석]
Hanja[edit]
Compounds[edit]
- 석유 (石油, seogyu)
- 석탄 (石炭, seoktan)
- 석류 (石榴, seongnyu)
- 운석 (隕石, unseok)
- 암석 (巖石, amseok)
- 옥석 (玉石, okseok)
- 석회 (石灰, seokhoe)
- 반석 (盤石, banseok)
- 광석 (鑛石, gwangseok)
- 비석 (碑石, biseok)
- 초석 (礎石, choseok)
- 화석 (化石, hwaseok)
- 석탑 (石塔, seoktap)
- 자석 (磁石, jaseok)
- 휘석 (輝石, hwiseok)
- 석불 (石佛, seokbul)
- 투석 (投石, tuseok)
- 석재 (石材, seokjae)
- 보석 (寶石, boseok)
- 석굴 (石窟, seokgul)
- 금석 (金石, geumseok)
- 정석 (定石, jeongseok)
- 청금석 (靑金石, cheonggeumseok)
- 석기 (石器, seokgi)
- 석면 (石綿, seongmyeon)
- 석공 (石工, seokgong)
- 석각 (石刻, seokgak)
- 석조 (石造, seokjo)
Kunigami[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with Japanese 石 (ishi).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
石 (shī)
Miyako[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with Japanese 石 (ishi).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
石 (isu)
Okinawan[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with Japanese 石 (ishi).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
石 (ishi)
Old Japanese[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with 磯 (iso1, “pebble; gravel; rocky beach”).
Noun[edit]
石 (isi) (kana いし)
- a stone
- , text here
- 多良志比賣可尾能美許等能奈都良須等美多多志世利斯伊志遠多礼美吉
- tarasi pi1me1 kami2 no2 mi1ko2to2 no2 na turasu to2 mi1-tatasi serisi isi wo tare miki1
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
- [Note: Another version replaces na turasu to2 with 阿由都流等 (ayu turu to2, “catching sweetfishes”)
- , text here
Derived terms[edit]
Descendants[edit]
- Japanese: 石 (ishi)
Vietnamese[edit]
Han character[edit]
石: Hán Việt readings: thạch[1][2][3], đán[3]
石: Nôm readings: thạch[1][2], sạch[1]
References[edit]
Yaeyama[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with Japanese 石 (ishi).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
石 (isï)
Yonaguni[edit]
Kanji[edit]
Etymology[edit]
Cognate with Japanese 石 (ishi).
Pronunciation[edit]
Noun[edit]
石 (ichi)
References[edit]
- “いち【石】” in JLect - Japonic Languages and Dialects Database Dictionary, 2019.
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han pictograms
- Chinese terms with unknown etymologies
- Mandarin terms with audio links
- Cantonese terms with audio links
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese Han characters
- Chinese nouns classified by 嚿
- Chinese nouns classified by 塊/块
- Cantonese Chinese
- Chinese surnames
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Mandarin terms with multiple pronunciations
- Japanese Han characters
- Grade 1 kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading じゃく
- Japanese kanji with historical goon reading じやく
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading せき
- Japanese kanji with tōon reading しく
- Japanese kanji with kan'yōon reading こく
- Japanese kanji with kan'yōon reading しゃく
- Japanese kanji with historical kan'yōon reading しやく
- Japanese kanji with kun reading いし
- Japanese kanji with kun reading いわ
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading いは
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading あつ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading いさ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading いす
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading いそ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading かた
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading し
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading せっく
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading と
- Japanese terms spelled with 石 read as いし
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms written with one Han script character
- Japanese terms spelled with 石
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Japanese terms with usage examples
- Japanese slang
- ja:Electronics
- Japanese terms spelled with 石 read as こく
- Japanese terms read with on'yomi
- Japanese terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Japanese terms with historical senses
- Japanese terms spelled with 石 read as せき
- Japanese counters
- Japanese affixes
- Japanese short forms
- ja:Rocks
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Korean lemmas
- Korean Han characters
- CJKV radicals
- Kunigami Han characters
- Kunigami kanji with kun reading しー
- Kunigami terms with IPA pronunciation
- Kunigami lemmas
- Kunigami nouns
- Kunigami terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Kunigami terms written with one Han script character
- Kunigami terms spelled with 石
- Kunigami single-kanji terms
- Miyako Han characters
- Miyako kanji with kun reading いす
- Miyako terms with IPA pronunciation
- Miyako lemmas
- Miyako nouns
- Miyako terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Miyako terms written with one Han script character
- Miyako terms spelled with 石
- Miyako single-kanji terms
- Okinawan Han characters
- Okinawan terms with IPA pronunciation
- Okinawan lemmas
- Okinawan nouns
- Okinawan terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Okinawan terms written with one Han script character
- Okinawan terms spelled with 石
- Okinawan single-kanji terms
- Old Japanese lemmas
- Old Japanese nouns
- Old Japanese terms with usage examples
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom
- Yaeyama Han characters
- Yaeyama kanji with kun reading いしぃ
- Yaeyama terms with IPA pronunciation
- Yaeyama lemmas
- Yaeyama nouns
- Yaeyama terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Yaeyama terms written with one Han script character
- Yaeyama terms spelled with 石
- Yaeyama single-kanji terms
- Yonaguni Han characters
- Yonaguni kanji with kun reading いち
- Yonaguni terms with IPA pronunciation
- Yonaguni lemmas
- Yonaguni nouns
- Yonaguni terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Yonaguni terms written with one Han script character
- Yonaguni terms spelled with 石
- Yonaguni single-kanji terms

